PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES (50% SOLUTION)
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
REFRACTIVE INDEX
None
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
59.5% min
LEAD CONTENT
500g/l min
FREE MSA
3.0% max
|
|
|
| LEAD METHANESULFONATE | ||
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | ||
| CAS NO. | 17570-76-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 401-750-5 | |
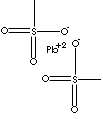
| FORMULA | (CH3SO3)2Pb | |
| MOL WT. | 397.38 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Methanesulfonic acid, lead(2+) salt; | |
| Lead(II) methanesulfonate; | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES (50% SOLUTION) |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear liquid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.64 | |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.4230 | |
| NFPA RATINGS |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
None | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Electroplating is a process for applying a metallic coating on a metal surface by electrodeposition from a suitable electrolyte solution for imparting corrosion resistance and direct production of printed circuit boards without etching out of a piece of copper sheet. The object to be plated is connected as the cathode in the electrolyte solution and then passing electric current is passed through the anode which causes the ions to be deposited to the material. Methanesulfonic acid is used as the acid electrolyte in the electroplating because many metals which are not soluble in mineral or organic acids are soluble, particularly tin and lead plating. Stannic sludge formation is rare as methanesulfonic acid is a non-oxidizing acid. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
| 60% SOLUTION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear liquid | |
| (CH3SO3)2Pb |
59.5% min | |
|
LEAD CONTENT |
500g/l min | |
|
FREE MSA |
3.0% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 30kgs in plastic drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
|
||
|
|
|